Best Diet Foods for Weight Loss: The Ultimate Evidence-Based Guide
Published: December 20, 2025
Losing weight in 2025 isn't about chasing fads or starving yourself—it's about choosing smart, nutrient-dense foods that keep you full, boost your metabolism, and support long-term health. The science is clear: sustainable weight loss comes from creating a moderate calorie deficit while prioritizing foods high in protein, fiber, and water content.
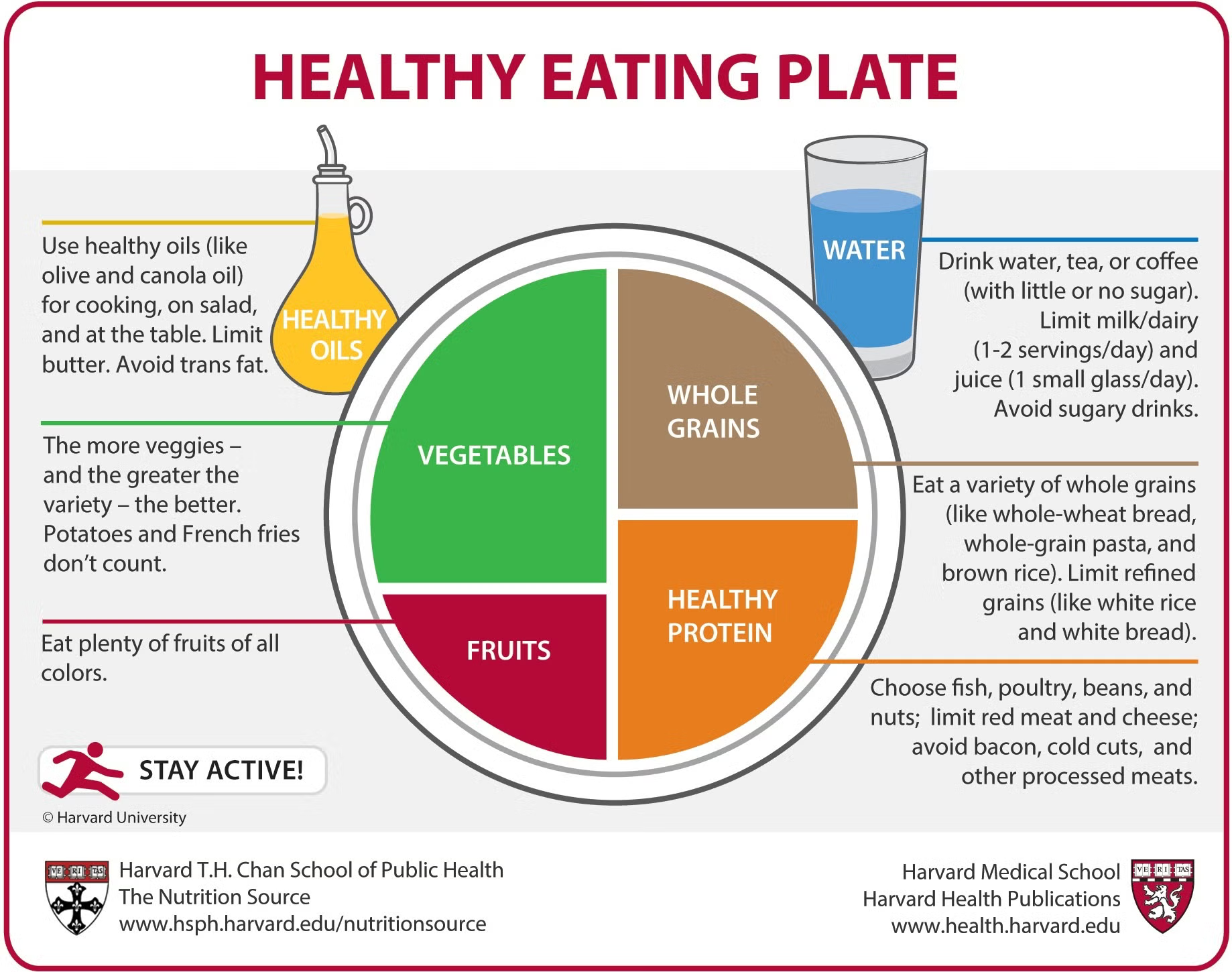
These foods increase satiety, enhance fat oxidation, and help preserve muscle mass, making the process feel effortless rather than punishing.Recent 2025 reviews from sources like Healthline, Harvard Nutrition Source, and the Journal of Obesity confirm that diets rich in whole foods—such as lean proteins, vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and healthy fats—lead to greater weight loss and better adherence compared to restrictive plans.
The Mediterranean diet, consistently ranked #1 by U.S. News & World Report for 2025, emphasizes these foods and supports not just weight loss but also heart health, reduced inflammation, and longevity.In this detailed guide, we'll explore the top evidence-based diet foods for weight loss, backed by 2025 studies. You'll learn why they work, how to incorporate them into meals, and practical tips for success. Whether you're aiming for 5 kg or 20 kg loss, these foods form the foundation of any effective plan.
Why Food Choice Matters More Than Calories Alone
Calories in vs. calories out is the basic equation, but food quality determines how sustainable and healthy your weight loss is. High-volume, low-calorie foods (like vegetables) allow you to eat more while staying in deficit. Protein-rich foods preserve muscle, boosting your resting metabolic rate. Fiber slows digestion, stabilizing blood sugar and reducing cravings.A 2025 study in Nutrients showed that diets emphasizing these foods led to 17% more weight loss over 12 months compared to calorie-matched low-nutrient diets. The key? Satiety—feeling full on fewer calories.
The Top Evidence-Based Foods for Weight Loss in 2025
1. Leafy Greens and Non-Starchy Vegetables
Vegetables like spinach, kale, broccoli, and zucchini are weight-loss superstars. They're extremely low in calories (20–50 per cup) but high in fiber, water, and nutrients. Eating more vegetables increases meal volume without adding calories, leading to natural portion control.
Studies from Harvard's Nutrition Source (2025 update) show that increasing vegetable intake by one serving daily correlates with 0.25 kg weight loss over four years. Broccoli's sulforaphane may even enhance fat burning.
How to Eat More: Fill half your plate with greens. Roast broccoli with olive oil, add spinach to smoothies, or make zucchini noodles.
2. Lean Proteins (Chicken, Fish, Eggs, Turkey)
Protein is the most satiating macronutrient, reducing hunger hormones like ghrelin by up to 25% (2025 Obesity Reviews). It also has a high thermic effect—your body burns 20–30% of protein calories during digestion.
Lean sources like chicken breast, salmon, eggs, and turkey preserve muscle during deficit, keeping metabolism high. A 2025 trial in the International Journal of Obesity found high-protein diets (1.6–2.2 g/kg) led to 4 kg more fat loss than standard protein intake.
How to Incorporate: Aim for protein at every meal. Grill chicken for salads, bake salmon with herbs, or boil eggs for snacks.
3. Whole Grains (Oats, Quinoa, Brown Rice)
Whole grains provide sustained energy and fiber, stabilizing blood sugar and preventing overeating. Oats' beta-glucan slows digestion, promoting fullness.
The 2025 U.S. News diet rankings highlight whole grains in top plans like Mediterranean. A meta-analysis showed whole grain consumers lose 0.5–1 kg more than refined-grain eaters.
How to Use: Start days with oatmeal topped with berries, swap white rice for quinoa, or add barley to soups.
4. Legumes (Beans, Lentils, Chickpeas)
Legumes are fiber and protein powerhouses—cheap, versatile, and incredibly filling. A cup of lentils has 18 g protein and 16 g fiber for only 230 calories.
2025 research in Nutrients links legume intake to lower BMI and waist circumference. They improve gut health, aiding weight management.
How to Enjoy: Add chickpeas to salads, make lentil soup, or blend black beans into dips.
5. Berries and Low-Sugar Fruits
Berries (strawberries, blueberries, raspberries) are low-calorie antioxidant bombs. Their fiber and polyphenols reduce inflammation linked to fat storage.
Harvard studies (2025) associate berry consumption with slower weight gain. Apples and pears also rank high for pectin fiber.
How to Include: Snack on berries, add to yogurt, or blend into smoothies.
6. Greek Yogurt and Low-Fat Dairy
Full-fat or low-fat Greek yogurt provides 20–25 g of protein per serving with probiotics for gut health. 2025 reviews show dairy protein supports muscle retention during loss.
How to Eat: Plain Greek yogurt with berries and nuts for breakfast or a snack.
7. Nuts and Seeds (in Moderation)
Almonds, walnuts, and chia seeds offer healthy fats, protein, and fiber. Though calorie-dense, studies show nut eaters have lower BMI due to satiety.
A 2025 trial found 30 g of daily almonds aided fat loss without calorie restriction.
How to Portion: 1 small handful (28 g) as a snack.
8. Fatty Fish (Salmon, Mackerel)
Omega-3s in fatty fish reduce inflammation and improve insulin sensitivity. Protein content promotes fullness.2025 Mediterranean diet rankings highlight fish for heart health and weight control.
How to Prepare: Bake salmon twice weekly.
9. Eggs
Eggs are nutrient-dense with high-quality protein. Studies show egg breakfasts reduce calorie intake later.
How to Use: Boiled, poached, or omelets with veggies.
10. Green Tea and Coffee
Catechins in green tea and caffeine boost metabolism slightly (50–100 extra calories/day).
2025 reviews confirm modest fat oxidation benefits.
How to Drink: 2–4 cups of green tea
Practical Tips for Success in 2025
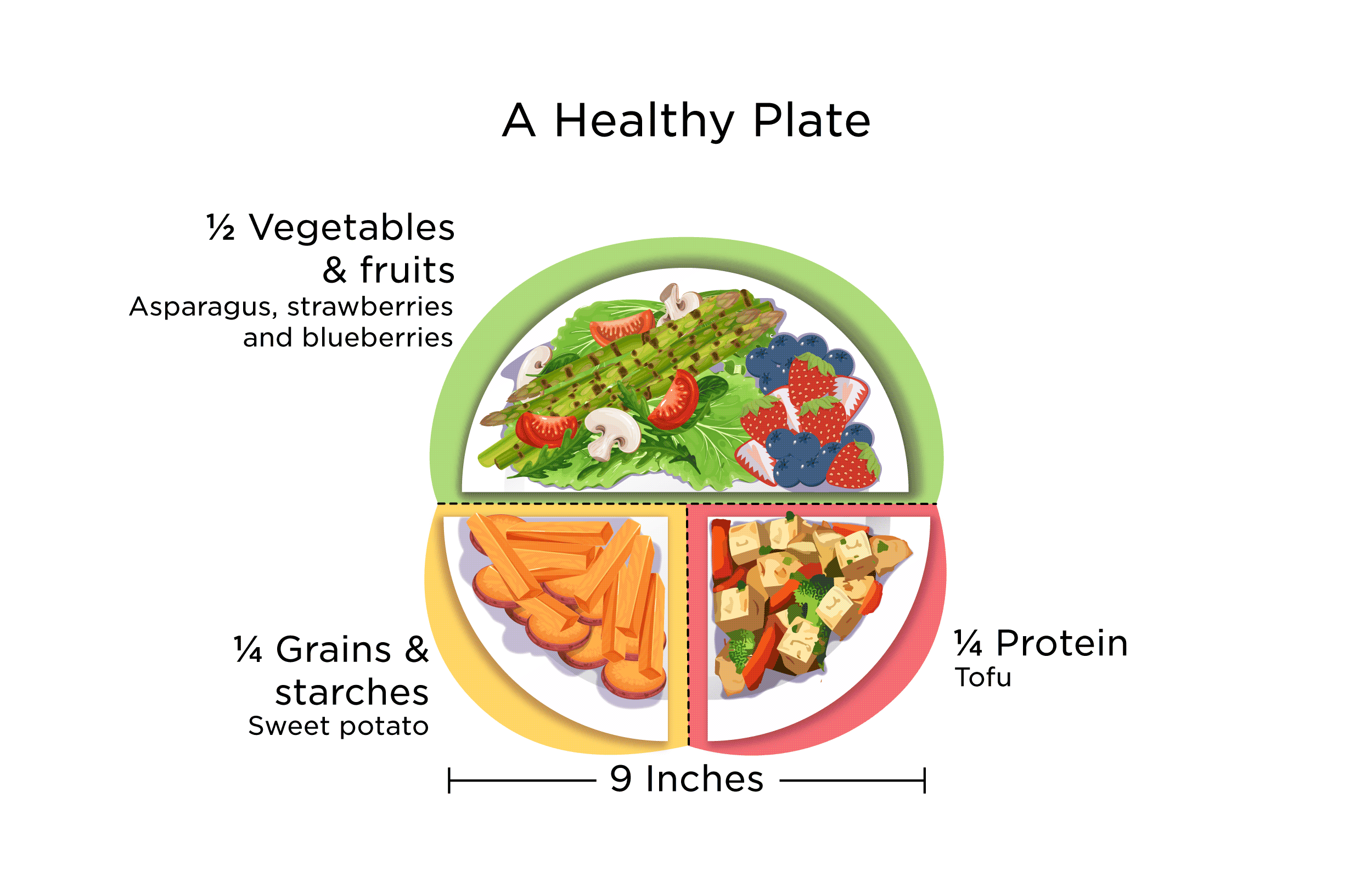
Build meals around these foods: half a plate of vegetables, a quarter of protein, a quarter of whole grains. Track progress with apps, but focus on habits. Combine with strength training and walking for the best results. Stay hydrated—water aids metabolism.
Conclusion: Sustainable Over Quick
The best diet foods for weight loss are whole, minimally processed ones that nourish and satisfy. No magic pill—just consistent choices.
Start small: Add one new food this week. Your body will thank you.
Consult a professional for personalized advice.


